Feeling Overwhelmed? Here’s How Your 5 Senses Can Help You Feel Safe Again
Have you ever been caught in a wave of anxiety, in a room full of noise, your chest tightening, thoughts spiraling? Perhaps your surroundings felt too loud, too bright, or too overwhelming. I’ve been there. And what pulled me out of that storm wasn’t a complicated ritual. It was a moment of noticing: the cool, steady feel of a glass of water in my hand. That single sensation grounded me. It reminded me that I was here, that I was safe. That’s the power of sensory grounding techniques, and it’s something you can learn to use, too. In today’s hyper-connected, overstimulated world, your brain is constantly scanning for threats. Even when you’re physically safe, your nervous system might be firing off alarms. This is where the 5 senses anxiety relief method steps in, offering you practical tools to come back to the present and regain control.
What Is Sensory Grounding? Understanding the 5 Senses Anxiety Relief Method
A Quick Definition of Sensory Grounding Techniques
Sensory grounding is a mindfulness practice that uses your five senses, sight, sound, touch, smell, and taste, to bring your awareness back to the present.
These techniques help you disengage from anxious thought loops by focusing on tangible, physical sensations. Instead of staying stuck in your head, you return to your body.
It’s especially helpful when anxiety feels overwhelming, but it’s also a powerful daily habit to reduce stress and improve emotional resilience.
Why It Works: The Science Behind Sensory Grounding
When you feel anxious, your brain activates the amygdala, the center of fear. This triggers the fight-or-flight response, even if there’s no real danger.
Grounding practices stimulate the prefrontal cortex, the area responsible for reasoning and decision-making. They also support your parasympathetic nervous system, which calms the body.
Research tied to polyvagal theory, somatic experiencing, and trauma-informed care all support the use of sensory grounding. It redirects your attention from emotional overwhelm to safety signals in your environment.
How to Use Each of the 5 Senses for Anxiety Relief

Let’s break it down by sense. You might find that one or two work better for you than others. That’s normal; grounding is highly personal.
Grounding with Sight 👁️
Visual Techniques to Calm an Overactive Mind
- Look around and name 5 things you can see
- Focus on a calming object: a favorite photo, plant, or piece of art
- Watch clouds or nature scenes outside
- Use soft, warm lighting instead of harsh fluorescents
- Try color therapy: focus on soothing tones like blue or green
Grounding with Sound 🎧
Audio Strategies for Re-centering
- Listen to a calming playlist or ambient sounds
- Identify 4 sounds around you: birds, cars, footsteps, wind
- Repeat a grounding phrase or affirmation: “I am safe.”
- Use guided meditations or nature sound apps
Grounding with Touch ✋
Physical Sensations That Anchor You
- Grab a textured object: stone, fabric, bracelet, or fidget tool
- Run cold or warm water over your hands
- Use temperature contrast: hold an ice cube or heat pack
- Self-soothing gestures: place a hand over your chest or rub your palms
Grounding with Smell 🙃
Aromatherapy and Everyday Scents
- Inhale essential oils like lavender, eucalyptus, or citrus
- Smell familiar objects: your pillow, coffee, or a favorite book
- Light a scented candle or burn incense
- Bake or cook something aromatic
Grounding with Taste 😋
Engaging Taste to Stay Present
- Sip herbal tea slowly, noticing flavor and temperature
- Eat a small snack mindfully: dark chocolate, citrus fruit, or mints
- Try a sharp taste like lemon or ginger to jolt your awareness
- Chew gum and focus on texture and taste
Quick Sensory Grounding Routine (5-4-3-2-1 Method)

A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The 5-4-3-2-1 technique is a classic and effective way to ground yourself quickly.
Here’s how it works:
- 5 things you can see
- 4 things you can touch
- 3 things you can hear
- 2 things you can smell
- 1 thing you can taste
Go slowly. Let yourself pause at each step. You’re telling your brain: “We’re okay. We’re here.”
When and Where to Use It
- During a panic attack
- In an overstimulating environment (airport, crowd, noisy room)
- Before bed when your thoughts won’t stop
- During a flashback or episode of dissociation
It works for children, teens, and adults; just adjust based on their preferences and understanding.
Grounding Recipes to Support the 5 Senses
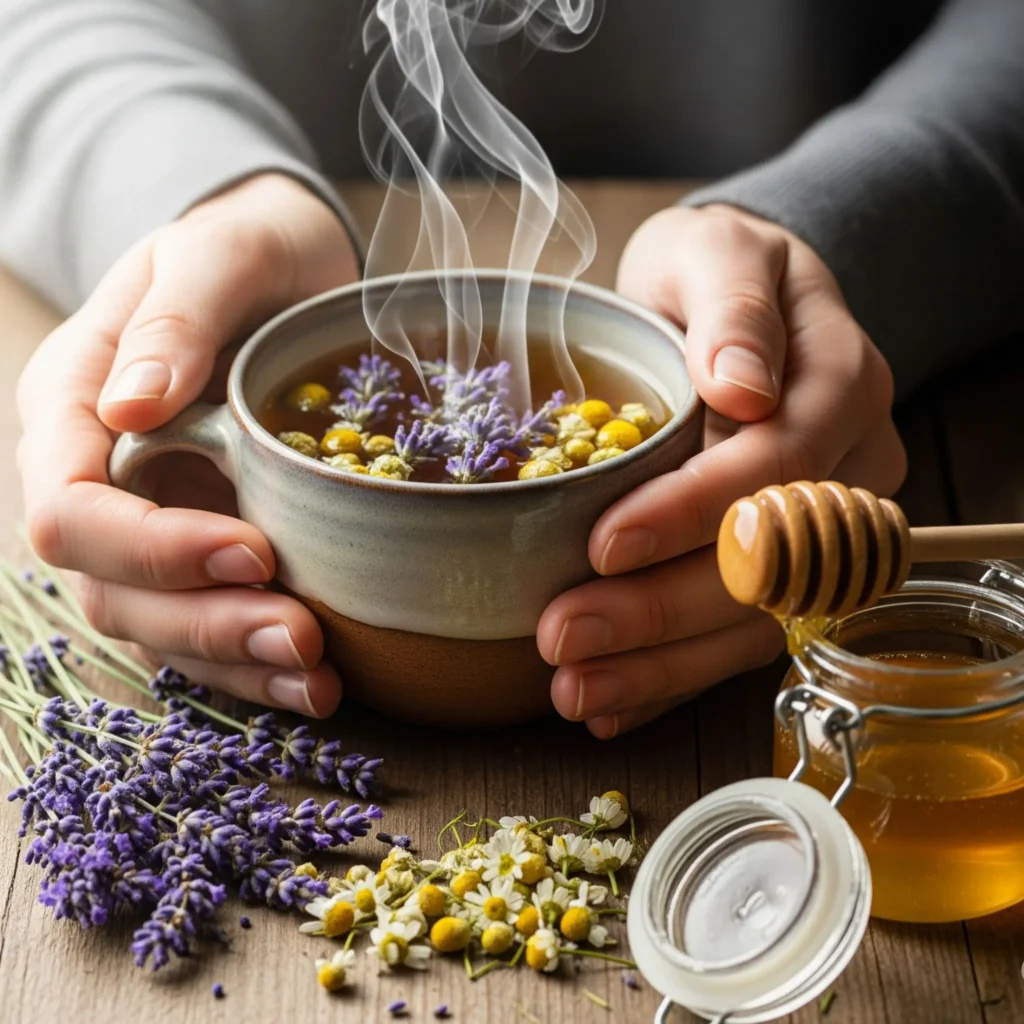

Food and scent are powerful allies in grounding. Here are two simple recipes that combine aroma, flavor, and mindfulness.
Aromatic Herbal Tea for Smell and Taste Relief
| Ingredient | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Dried lavender buds | 1 tsp |
| Chamomile flowers | 1 tsp |
| Honey (optional) | 1 tsp |
| Hot water | 1 cup |
Steps:
- Add the dried herbs to a tea infuser.
- Pour hot water and steep for 5–7 minutes.
- Add honey if desired.
- Sip slowly. Focus on the warmth, scent, and flavor.
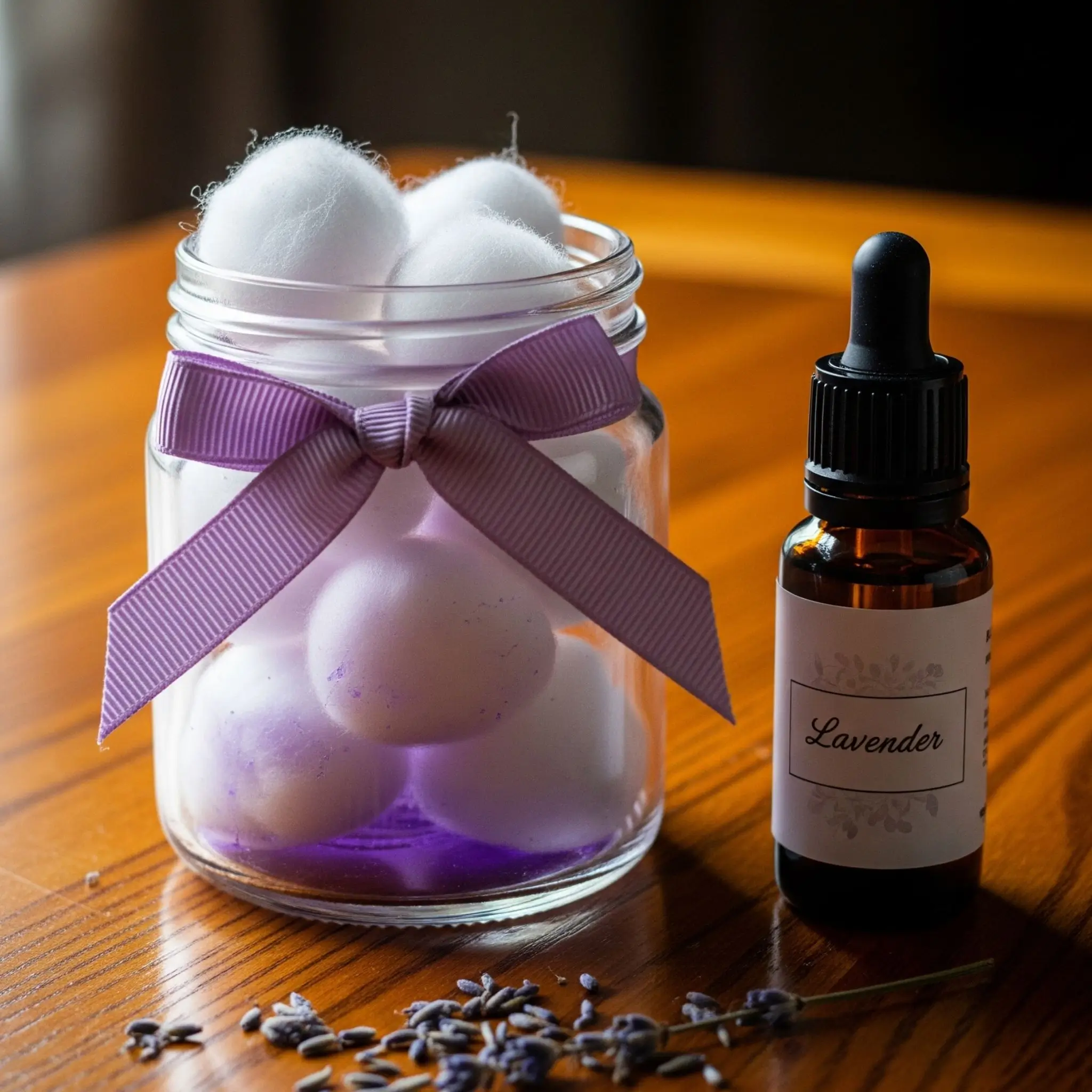
DIY Scent Jar for Instant Grounding
| Ingredient | Use |
|---|---|
| Small mason jar | Container |
| Cotton balls | Holds essential oil |
| Lavender oil | Calming scent |
| Label or ribbon | Personalize it |
Instructions:
- Soak cotton balls in a few drops of essential oil.
- Place them inside the jar.
- Open and inhale the scent as needed for grounding.
When to Use Sensory Grounding Techniques

Everyday Stress vs. Chronic Anxiety
- Everyday stress: Try simple techniques like 5-4-3-2-1 or grounding tea
- Chronic anxiety or PTSD: Use grounding with professional support (therapist, coach)
These tools aren’t meant to replace therapy, but they can complement other treatments and give you daily control.
Helpful Situations
- Public speaking nerves
- Work stress or burnout
- Emotional overwhelm
- Social anxiety events
- Transitions (moving, breakups, change)
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
What Not to Do
- Forcing a sense that isn’t working for you (e.g., trying to smell something when you can’t)
- Rushing through the steps, grounding works best when done slowly
- Expecting instant transformation
Tips for Effectiveness
- Start practicing during calm moments to build the habit
- Combine grounding with deep breathing or gentle movement
- Track which sense works best for you in different moods
FAQ – Sensory Grounding Techniques for Anxiety Relief
Can sensory grounding help with panic attacks?
Yes. It gives you a practical, immediate way to return to the present when your body feels hijacked by fear.
How often should I practice sensory grounding?
Aim for 2–5 minutes daily. Consistency builds confidence and effectiveness.
Can I use sensory grounding with kids?
Definitely. Use playful elements like colorful objects, calming scents, or favorite snacks. Let them guide what feels good.
What if one of my senses is impaired?
Sensory grounding is flexible. Focus on the senses that are most accessible to you.
Conclusion: Reset, Refocus, Reclaim Calm Through Your 5 Senses
You don’t need complex tools, hours of meditation, or perfect conditions to feel calmer. Everything you need is already with you. Your five senses are powerful tools, and they’re always available.
Sensory grounding techniques offer more than just anxiety relief. They help you become more present, more connected, and more in tune with your body. In a world that constantly pulls you away from yourself, grounding brings you back.
Call to Action:
Try one sensory grounding method today. Notice what works for you. Keep it simple, stay curious, and journal your experience. Over time, you’ll build your own personalized toolkit for peace. ➤
Small steps lead to big shifts. And every moment you come back to yourself is a victory.